- Home >
- About Us >
- Corporate Governance and Internal Control >
- Internal Control : Risk Management
Internal Control
Risk Management
Basic Recognition
To ensure sound and proper business operations and to ensure that we fulfill the obligations arising from our insurance policies, we identify and evaluate potential risks, take appropriate action based on the specific characteristics of each risk and comprehensively manage those risks. We are committed, on a company-wide basis, to improving soundness through the management and control of those risk volume and capital.
We have also established a crisis management system and a risk management system to respond to catastrophes and large-scale disasters in addition to our everyday risk management system.
Risk Management Policies and Regulations
Our Basic Internal Control Policy includes our basic philosophy and policies regarding risk management. The approach used to manage each type of risk is developed in line with our series of Basic Risk Management Policies. In addition, each of the risk management regulations and standards is translated into practical rules, following our series of Basic Risk Management Policies.
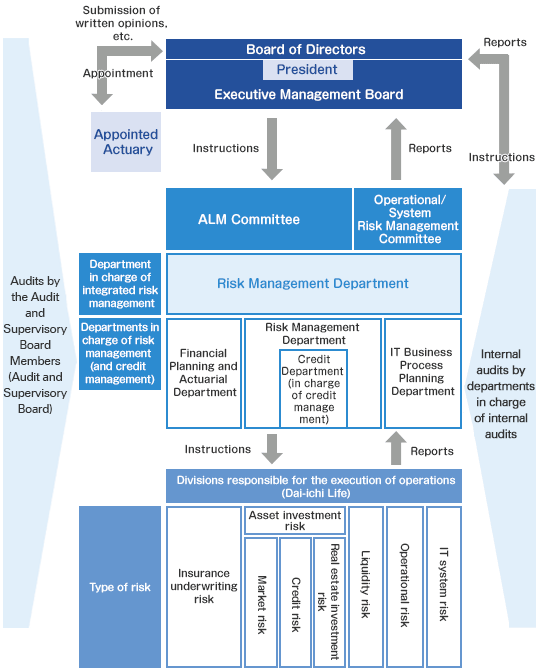
Risk Management Structures
For risks arising from operations of the Company, we developed a risk management structure in which the operations of the Company are monitored by the department responsible according to the risk category, in obedience to our series of Basic Risk Management Policies. To strengthen our risk management structure, we have established a Risk Management Department, which manages risks comprehensively, on a company-wide basis.
We have established the ERM Committee, Operational Risk Management Committee and System Risk Management Committee, each of which convenes regularly for management to share information regarding individual risks that will be used to guide decision making. Moreover, our Internal Audit Department examines the effectiveness and appropriateness of our risk management functions.
The status of risk management is reported to the Board of Directors, the Executive Management Board. Our Audit and Supervisory Board Members inspect overall risk management, including those taken by our management.
Promotion of ERM
The Company promotes Enterprise Risk Management (ERM), a risk management approach to promote business activities, by formulating a management plan and capital strategies in accordance with its capital, risk, and profit situation.
When formulating a management plan and capital strategies as a risk management measure related to ERM, the Risk Management Department examines the adequacy of the plan and the strategies, properly controls capital, risks, and profits by setting and managing risk tolerance, taking into consideration the source, types, and characteristics of risks, and promotes the enhancement of the risk management.
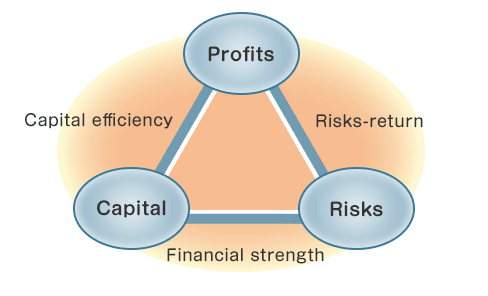
The Company controls the integrity of the group through activities such as consolidating different types of risk and making capital provision on an economic value, book value, and regulatory basis. The management of risk on the basis of economic value is conducted using embedded value (an indicator used by life insurance companies to represent corporate value) and coherent risk assessment techniques.
To identify and evaluate aspects that are not captured by the model-based quantification of risk, stress testing is conducted using worst-case scenarios based on possible future events or actual past events, such as financial market panics or large natural disasters. This is then used as a basis for analyzing the factors that influence the integrity of the organization and reporting the results to the board of directors, executive management board, and others, and for considering and implementing management and financial measures and ways to improve monitoring of market and other conditions as required.
CSA (control self-assessment) initiatives
Dai-ichi Life has continued to work towards improving management quality in an aim to be a company that will continue to be trusted and selected by customers. As part of these efforts, a CSA (control self-assessment) is carried out by all head office departments and branches according to standardized and systemized risk identification and analysis methods, covering primarily administration risks, system risks and other operational risks.
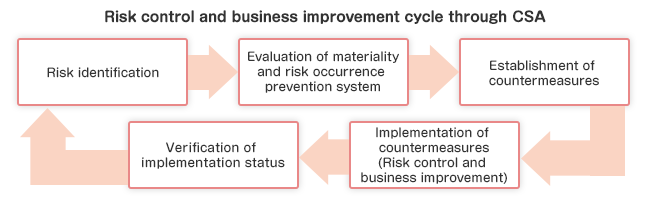
CSA consists of activities that promote risk control and business improvement by implementing the cycle displayed above that starts with the identification of risks inherent in our business. A wide range of risks is covered, including administration risks, system risks, and compliance risks.
As part of our DSR management efforts, the entire Group implements activities to promote risk control and operational improvements as it works to gain further trust and support from customers.
Efforts at head office departments
The level of risks for each operation is assessed by identifying the risk for each operation, assessing the materiality of these risks by considering the impact on customers and the scale of losses in the event that the risks arise, and also assessing the systems for preventing such risks. After conducting this process, countermeasures are established and implemented to prepare for the occurrence of such risks and in consideration of the scale of risks as part of our risk control and business improvement efforts as we promote appropriate business operations.
Efforts at branch offices
Because the operations of each branch are fundamentally the same, the head office identifies and summarizes the risks to be targeted by CSA, while each branch focuses on the assessment of systems to prevent the occurrence of risks and the implementation of countermeasures.
Business Continuity Management
Dai-ichi Life has established the Large Scale Risk Management Committee to constantly prepare for the future to ensure that risks are managed individually and that services provided to our customers can be continued even after a major earthquake, other large-scale disaster or a pandemic caused by a new influenza virus.
Specifically, measures are maintained appropriately for crisis management including business continuity planning, and multiple redundancies have been used to backup system and customer data to ensure insurance administrative processes remain working and payouts can be made smoothly even if the head office or branch offices suffer damage. We also provide training and hold drills to achieve continual improvements in our business continuity management.
Following the Great East Japan Earthquake that struck on March 11, 2011, we immediately set up a Disaster Response Headquarters led by the President of Dai-ichi Life, in accordance with our business continuity plan created before the earthquake, and each organization took the time to confirm the safety of employees and to assist damaged branches in getting back up and running in a prompt manner. At the same time, we mobilized Total Life Plan Designers, agents, as well as staff from our branches and head office to check the safety of customers using a company-wide effort and to open temporary contact points for customers in the disaster zone to respond to customer needs locally.
Additionally, in order to stably provide customers with services including payments of claims and benefits and maintain operations even during pandemics of influenza with high levels of contagion, we have established the Pandemic Influenza Countermeasure Action Plan and the Pandemic Influenza Countermeasure Basic Manual to stipulate group-wide measures concerning business continuity, and efforts are also being made to accumulate mitigation materials such as masks and antiseptic solution.
We are committed to continually reinforcing our security measures and preparations for large-scale disasters to further promote business continuity management.

